SAM-TB
Home
My data
My analysis
My samples
Help
FAQ
中文
Sign in
##Reconstruct phylogenetic trees ###Operating instructions (1) Create analysis: ① Click “+ New analysis” and select “Reconstruct phylogenetic trees”. The page will jump to the “Home” page of phylogenetic tree reconstruction. ② Click “+Select sample” to select samples, or click “+Batch add” and enter the ID in the floating window to add samples (≥4 samples) for phylogenetic tree reconstruction. Note:only samples whose "Single sample variants analysis" have been completed can be selected or added for the phylogenetic tree reconstruction. If a sample has been analyzed multiple times, only the most recent result will be used. If the number of samples exceeds 500, the analysis using the maximum likelihood method will be very slow. ③ Click “Modifiable Parameters” at the bottom right of the page to view or modify parameters, and click “Start” to begin the analysis. 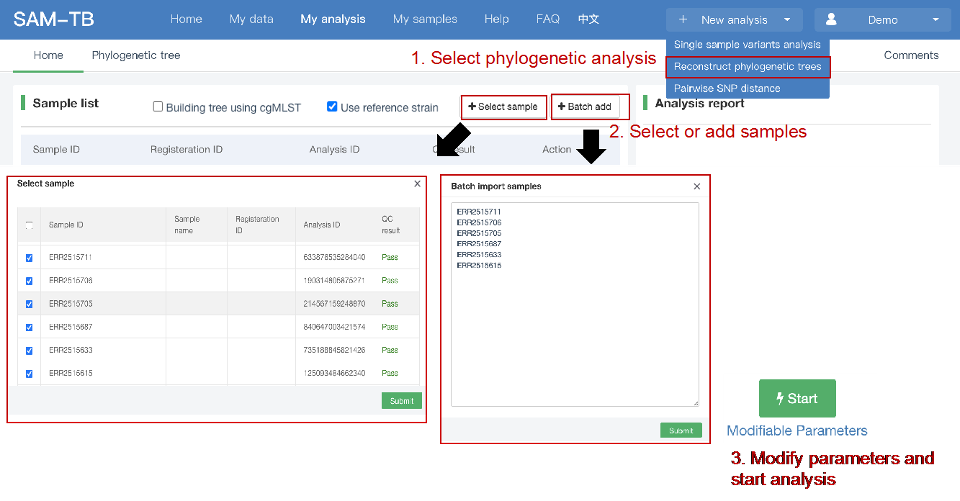 Note: 1. Click "Use reference strain" to select the reference strain(s) used for phylogenetic tree reconstruction. The references include strains of different subtypes of L1-6, M. bovis, and M. canettii (which can be used as the root). The "QC result" column shows whether the QC of the sample is adequate for constructing a phylogenetic tree. Any sample where the QC "Failed" may affect the results of the phylogenetic tree construction, and generally should not be included. 2. Click “Building tree using cgMLST” to reconstruct trees based on cgMLST rather that SNP. You have the option to select from two construction algorithms: the "Neighbor-Joining" and the "Minimum Spanning Tree".  (2) Stop the analysis: any analysis with the status “Running” can be stopped by clicking “Stop” at the bottom of the page. (3) Reanalyze: any analysis with status “Completed” can be redone in the following ways: ① If you don't want to change the samples used for phylogenetic tree reconstruction, click “Modifiable Parameters” in the page to modify parameters and “Restart” to reconstruct the phylogenetic tree. ② If you want to delete several samples from the phylogenetic tree reconstruction, click and enter the webpage of “Phylogenetic tree”. Check the samples to be included. Select “Use reference strain” or “Not use reference strain”, and the construction method “ML” (Maximum Likelihood) or “MP” (Maximum Parsimony). Click “Update” to reconstruct the phylogenetic tree. Return to the “Home” page to view the analysis process. 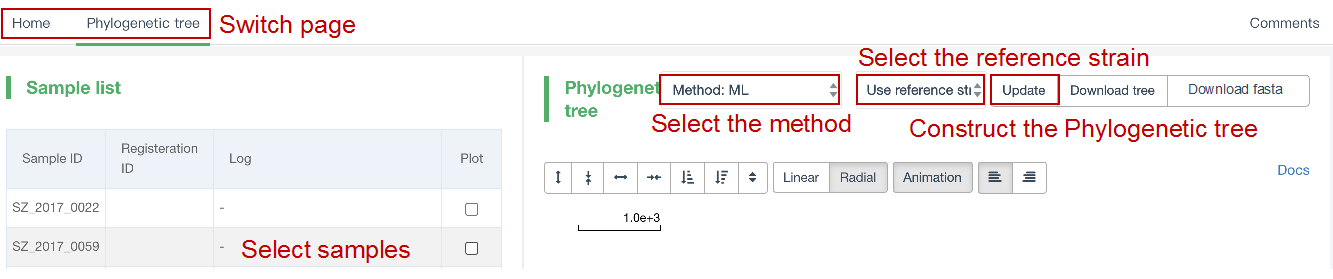 Note: when reanalysis is performed, the old results will be overwritten. ###Explanation of results After the analysis is successfully completed, you can switch to different result pages by clicking on “Home” and “Phylogenetic tree” in the secondary navigation bar. (1) The “Home” page shows the samples selected to construct the tree on the left, along with the option to choose whether to build the tree based on cgMLST; and the analysis logs on the right. 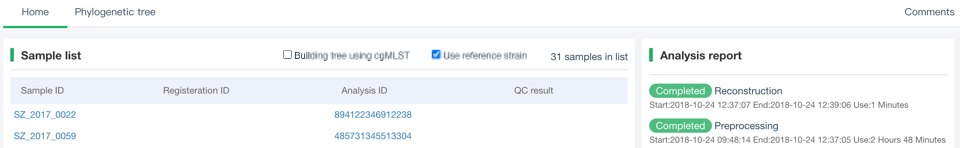 (2) The “Phylogenetic tree” page shows the samples used to construct the tree and the figure of the phylogenetic tree. Click "Download tree" on the right side of the page to download the newick file of the phylogenetic tree. The file can be imported into phylogenetic tree annotation tools to improve and annotate the figure presentation. Click on the "Download fasta" to download the alignment sequence for tree construction (specifically for tree building based on SNP); Click on the “Download Distance matrix” to download the distance matrix file used for tree construction (specifically for tree building based on cgMLST). 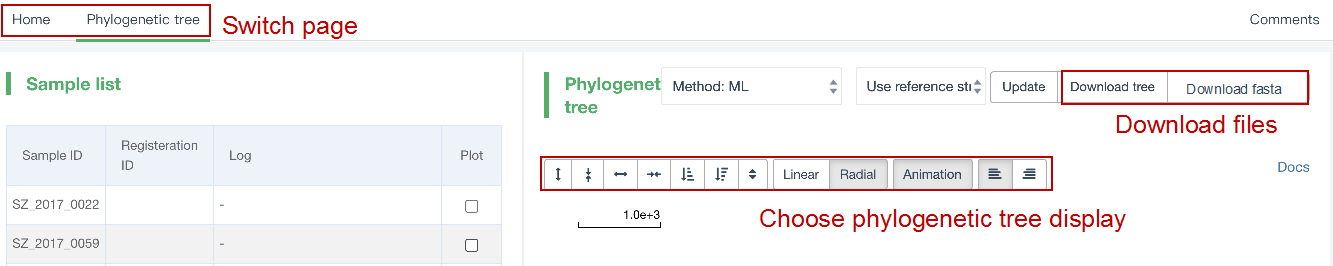 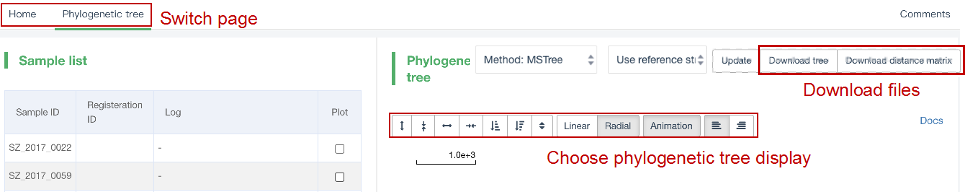 3) To alter the phylogenetic tree display: ① Click the strain name in the figure of phylogenetic tree to edit the tree. Select “incident branch” and “path to root” to show the path in a separate color, click “reroot on this node” to root the tree here, and choose “hide this node” to hide the terminal branch where the strain is located. Note: if two strains share a certain path, the specific color of the overlapping path will be cancelled when the paths of the two strains are displayed at the same time. ② You can also click a node in the figure of phylogenetic tree to edit the tree. Select “all descendant branches”, “all terminal branches” or “all internal branches” to show the corresponding branches of the node. Click “reroot on this node” to root the tree on the node. Choose “hide this subtree” to hide all branches under the node. Click the hidden node and select “show all descendant nodes” to cancel the hide operation. 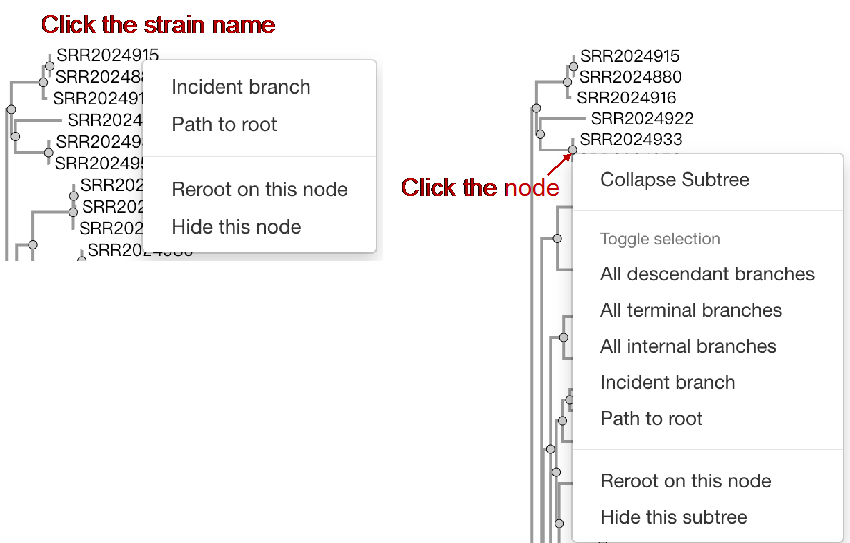 Note:refresh the page will restore the tree to its initial state. This website does not support further annotation of the phylogenetic tree. You can download the newick file and import it into other phylogenetic tree annotation tools such as Figtree, iTOL, treeview, GraPhlAn etc. to manipulate the figure. ###Interpretation of tree topology 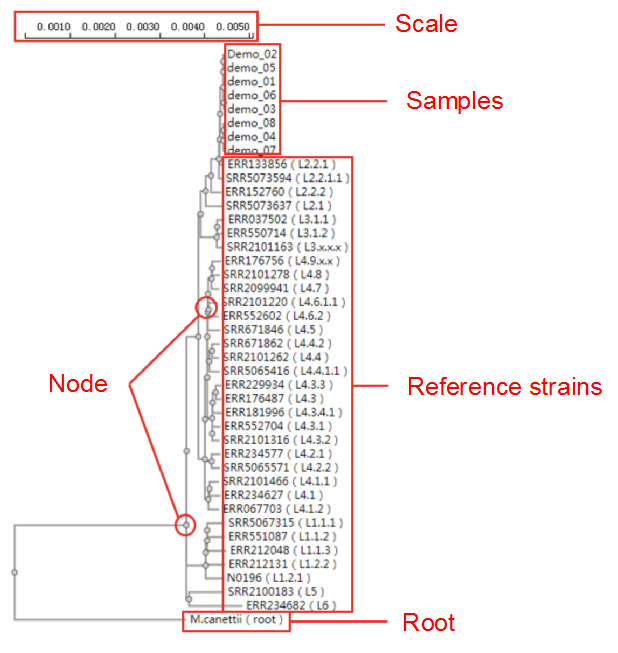 Root: the common ancestor of all branches; Node: represents a taxonomic unit (a collection of strains with certain common mutations); each open circle in the tree represents a node; Scale: the length indicates the degree of genetic variation and does not represent genetic distance. For example, 0.0010 means that the genetic variation of the genome is 0.0010. The calculation formula is: Variation = number of mutated bases/total bases (%); Samples: the samples used to construct the phylogenetic tree; Reference strains: the reference strains include strains of different subtypes of L1-6, M. bovis, and M. canettii (which can be used as the root). They can be used to view the position and genetic relationship of the analyzed samples in the phylogenetic tree.
<< Return
Title:
Description:
Thank you for using our service, we will reply you by email as soon as possible.